Knowledge bank
WEB is responsible for the supply of clean drinking water and reliable electricity on Bonaire. According to standard procedures we guard your health and safety. We are working hard on supply security, sustainability and affordability.
But our responsibility stops at your meter. WEB does not look behind your front door.
You are responsible for healthy and safe use of your installations for water, wastewater and electricity. Furthermore, you can do much yourself to save on water and electricity. It is sustainable and saves you money.
In this section we are pleased to inform you about health, safety and risk prevention. We also offer you handy practical saving tips.
Hidden
Hidden
Electricity and safety
WEB is responsible for a safe supply of electricity. For the safe use of electricity, you are responsible.
Important!
Always make sure that work on your electrical installation is realized by a registered installer. Otherwise in any case have the work done checked. In this way you will prevent problems and dangerous situations.
The registered installer is a specialist that inspects and assesses the work done by an electrician, or yourself, according to established standards.
A list of registered installers can be found here.
Download our folder safety (pdf). Or read the tips below.
Hidden
Hidden
Know what you buy
Electric appliances are manufactured as safe as possible. They have to measure up to various international standards. But there are also inferior appliances on the market.
Know what you buy!
Tips
- When purchasing, check the quality label: they guarantee that the safety has been checked by an independent institute.
- Preferably buy appliances with grounded cables and plugs. [link to >> Grounding] A grounded plug has notches embedded with metal strips (European system), or has three pins (American system).
- It is even better to buy double insulated appliances. Due to an extra insulated casing they do not discharge electricity in case of defects. These appliances can be recognized by an icon of two intertwined squares.
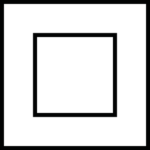
Know what you do
Even if you buy the best appliances, wiring, cables, plugs and electrical outlets: careless use leads to unsafe situations. The two most well-known are overload and short-circuiting. unfortunately, they are still often occurring.
Know what you are doing!
Overload and short-circuiting
Overloading of electric circuit happens because too many electronic appliances are used simultaneously. The electrical wires then overheat. The insulation melts, which causes short-circuiting.
Short-circuiting can also occur when an appliance or a cable is damaged. The copper kernels of the electricity cables can come into contact with each other. This results in a very high electrical current. The wiring overheats and the insulation melts.
In the case of short-circuiting the electricity will be disabled. A fuse will blow or a group switch will turn over. In serious cases the ground-fault circuit interrupter will turn over.
You will experience a partial or full power failure until the problem of short-circuiting is resolved.
Tips
Appliances
- Do not simultaneously use too many appliances. This involves ‘electricity guzzlers’ like washing machine, air conditioner, refrigerator, electric dryer, dishwasher or vacuum cleaner.
- Do not connect too many appliances to a single electrical outlet.
- Connect no more than 1200 Watts per single group in your meter box. On your appliances or in the manual you can see how many Watts an appliance uses. When in doubt, check with a registered installer.
- Always follow the operating instructions of electrical appliances.
Cables and plugs
- Check the insulation of electrical cables. Especially near the plug the insulation gets damaged. Fasten the plug again, or replace the appliance.
- Always hold the plug when removing it from the electrical outlet. Do not pull the cable, as this may damage the insulation.
- Do not ‘shut in’ cables, for example under a door or carpet. Also make sure that cables are always fully rolled out and do not touch each other and get tangled. This prevents overheating and wear and tear, which cause short circuit.
- Never use nails or staples to attach electrical cables. There are special cable clips to safely mount cables.
- Do not use electrical cables to hang anything from.
Do not use more than one extension cable between a device and the electrical outlet. The more cables, the greater the chance that they get tangled. Also by combining extension cables you can unconsciously connect too many appliances.
Provide grounding
Good grounding is important for your safety. Have your electrical installation grounded and have a ground-fault circuit interrupter placed in your meter box. Preferably buy appliances with grounded cables and plugs. But what precisely is grounding?
Ground fault
Grounding implies that there is an extra electricity wire that discharges the unwanted electricity via the earth. When that happens, we speak of a so-called ‘ground fault’. In your meter box the electricity will be disabled. A fuse will blow or a group switch or the ground-fault circuit interrupter will turn over.
Thunderstorm
When lightning strikes your electric appliances can be damaged. But if your electrical installation is well-grounded, the ground-fault circuit interrupter will turn over.
The electricity will be disabled. This prevents damage.
Appliances
Grounding is especially important for appliances with metal casing, like washing machines. If a cable or plug is worn out or disconnects, the connection cable of the electricity makes contact with the metal. Then the device gets electrified. Ground fault prevents this: The electricity will be disabled because in your meter box a fuse blows or a group switch or the ground fault circuit interrupter will turn over.
Beware!
If the ground wire is loose or missing, your appliances will keep working normally. Because of that a faulty grounding is often detected when things go wrong: the electricity is not discharged but electrifies the appliance.
Life-threatening
When an appliance is electrified this can cause fire or electrocute the user. That is life-threatening. Also think about this: moisture is an excellent conductor of electricity. Be especially careful in wet or humid environments such as the bathroom and kitchen.
Protect yourself, make sure appliances are grounded!
Tips
- Ask a registered installer to inspect or install your electrical system. Installation also includes the connection of appliances.
- Be careful with moisture. Do not place drinks or a vase with flowers on, or next to, electrical appliances.
- Preferably use appliances with grounded cables and plugs. Connect these only to grounded electrical outlets.
Please note!: Grounded outlets and plugs are required in humid rooms such as bathroom and kitchen.
Think about the children
Children are curious and love to move around. That makes safe electricity even more important. You must take measures to prevent accidents and dangerous situations: make electrical outlets childproof, make sure you have well insulated cables and plugs, move cables out of sight or make sure they are correctly secured.
Think about the children!
Tips
- Buy childproof electrical outlets. These are provided with plates that cover the openings of the electrical outlet. The plates only move if you push the plug with equal pressure on both openings. For you this is only a trick, for a child it is very difficult.
- You can cover your existing electrical outlets. For that they sell special loose cover plates. Please note: they are different for grounded and ungrounded electrical outlets! You stick or pinch the cover in the electrical outlet. A spring mechanism makes the openings of the electrical outlet invisible when not in use.
- After use of your appliances remove the plugs from the electrical outlets so that the cover plates are in the safe position.
- Regularly check the insulation of cables and plugs. A child does not know what bad insulation is and will just grab the cable. It may get an electrical shock.
- Move the electrical cables as much as possible out of sight. Your child could trip over or get tangled in it. Place cables alongside walls and behind furniture.
- Preferably use a cable duct. Another option is to secure cables on the baseboards with cable clips.
- Make sure hanging cables are not in reach of children. The child might take this as an invitation to play with the cable.
Legionella
Legionella is a bacterial species that may cause a contamination of drinking water. WEB does everything in its power to prevent legionella contamination. There are also measures you should take care of yourself. Legionella is a matter that concerns us all.
Download our folder Legionella (pdf). Or read the information below.
Hidden
Hidden
What is legionella?
Legionella appears wherever it is moist, in soil and in water. Legionella bacteria are as inevitable as all other types of bacteria. Also on Bonaire legionella is present in drinking water. The numbers are so small that the bacteria pose no threat.
Legionella bacteria grow in water with temperatures between 20 to 50 degrees Celsius (68 to 122 degrees Fahrenheit). There are 14 types of legionella bacteria, all of which appear in drinking water.
Where the water stands still legionella bacteria reproduce very rapidly. That occurs when there is a so-called ‘biofilm’ – a thin layer of micro organisms that is deposited on surfaces that are in contact with the water.
Wat is the Legionnaires’ disease?
The legionella bacteria cause pneumonia which is called Legionnaires’ disease. The name is derived from the first recognized outbreak in 1976 in the United States, amongst army veterans.
The Legionnaires’ disease should be treated with antibiotics as soon as possible. There is also a milder form, the legionella flu (Pontiac fever). This infection develops like a ‘normal’ flu and can clear up without treatment.
How do people get infected?
Infection occurs by aerosols, a mist of very small water droplets. Think of a shower, hot tub, steam bath or a fountain. Through inhaled contaminated aerosols legionella enters the respiratory tract. Then it can cause an infection. People do not get sick from drinking contaminated water. Legionella is not transferable from person to person.
Who are at most risk of getting sick?
The majority of people who get infected with legionella do not develop Legionnaires’ disease. Groups at increased risk of getting the disease are people from middle age, smokers, heavy drinkers and people with low resistance due to illness or old age.
What is the course of the disease?
The time between infection and becoming ill is between 2 and 18 days. Symptoms include headache, muscle pain, fatigue, high fever, coughing and shortness of breath. The Legionnaires’ disease should be treated with antibiotics as soon as possible. The milder form, the legionella flu, usually passes on its own.
What should I do to prevent legionella contamination?
There is no vaccination against Legionnaires’ disease. Note the following to reduce the risk of legionella:
- Most important is that water in pipes and drains in buildings and gardens does not stagnate too long. Rule of thumb: no longer than 7 days.
- Make sure all taps, showers, toilets and any sprinkler systems are regularly used.
Flush pipes and drains well if they have not been used longer than 7 days. Let garden hoses drain well after use.
- Clean hot tub, jacuzzi or humidifiers well according to the instructions. Decalcify showers regularly.
- Set water heaters properly: minimum at 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Is there anyone using an apnea device? Note that the water reservoir has to be filled with cooled boiled water. The water needs to be refreshed daily. The mask should be
cleaned daily. The tank must be cleaned and disinfected weekly.
Be alert!: Does the water have a strange smell, an aberrant color or is cloudy? Then something could be wrong.
Do you suspect contamination?
Call the emergency service number of WEB:
telephone 9215, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week available.
What does WEB do?
Half-yearly survey
WEB is legally obliged to inspect the drinking water every six months on legionella. We take samples of the entire production and distribution network, including the reservoirs. The water samples are subjected to bacteriological and chemical analyses. If we detect legionella above the standard of 100 colony-forming units per liter (100 cfu/l), WEB takes action. The pipe will be flushed and, if necessary, disinfected. If there is an intermediate suspicion of contamination, the water is promptly investigated.
Notification and information obligation
WEB is legally obliged to report a legionella contamination to the Human Environment and Transport Inspectorate (ILT), and to the people who might be affected. WEB must also make society aware of the dangers of legionella and give information how to reduce the risk of contamination.
Prevention
WEB takes prevention seriously. Information about legionella – and above all: the prevention of legionella contamination – we also distribute via a brochure, our Facebook page and radio and television spots. Prevention also is a matter that concerns us all!
Do not drip with the septic tank
WEB is regularly confronted with pollution of the drinking water by a cross connection. This is an illegal connection between the drinking water installation and the septic tank to drip the garden. It seems to be a nice cost reduction. But you are playing with your health – and the health of others. We are happy to explain you the health risks. We also strongly want to emphasize that cross connections are forbidden.
Download our folder Cross connection? No! (pdf). Or read the information below.
Hidden
Hidden
What is a cross connection?
A cross connection is the connection between the drinking water installation and the septic tank. With this the water from the septic tank can be used to water the garden. But water from your septic tank is untreated sewage water. Thus wastewater. That is a danger for the public health.
Watch the animation about Cross connection.
There is a high chance that the cross connection will cause a contamination of the drinking water. Not only in your own drinking water installation but also in the water supply network. A reverse flow, also known as ‘backflow’, can occur from your drainage system to your drinking water installation.
What is backflow?
Do you still remember the law of communicating vessels? When two vessels are connected, the fluid level of both vessels aims to be equal. If the level (pressure) in one vessel – your septic tank – lowers, then water from the other vessel – your drinking water installation – will flow over into the first one.
That was precisely the intention. But unfortunately: the reverse happens just as easily. Without noticing. The pressure in your septic tank will become higher than the pressure in your drinking water installation. Then sewage water flows back into your drinking water. That is backflow.
How does backflow cause contamination?
How can the pressure in your drainage system become higher than in your drinking water installation? There are various causes: height differences, the use of a pump, or intensive use of the drain. The backflow that arises contaminates your drinking water.
This contamination can easily end up in the water supply network. Because the pressure in the water supply network can be lower than in your drinking water installation. That occurs more often than you may think. Pressure differences occur very easily. Among other things at maintenance, closures, or by unexpected high water use, e.g. in fire fighting.
Each cross connection is a health risk!
Each connection between septic tank and drinking water installation is a public health risk. Therefore, in accordance with our Terms and Conditions 1992 the connection of the drinking water installation with any other water supply is not allowed.
WEB carries out random checks on cross connection. Violators will be disconnected and fined; also cleaning costs and possible repair and damage costs will be recovered on them.
Let’s do it together
WEB is responsible for the distribution of clean drinking water on Bonaire. Do you take your responsibility?
Avoid becoming a polluter and keep your septic tank and drinking water installation strictly separated. Keep our drinking water clean, for your health and the health of others!
Saving water
Did you know that per person we consume about 125 liters of drinking water per day. There are different ways to save water. Showering for one minute less, could save you five cubic meters water consumption. That comes down to saving you tens of dollars per year. The toilet accounts for 30% of our total water consumption. With a save button on your toilet tank it enables you to reduce the use of water by approximately 23 cubic meters of water.
Responsible use of water is better for the environment. It is also easier on the wallet!
Download our folder Saving (pdf). Or read the tips below.
Hidden
Hidden
Tips in the house
Toilet
- Adjust the float in the toilet tank so that the water tank does not fill completely.
• Are you not able to adjust the float? Then you can place a full two-liter bottle at the
bottom of the toilet tank (not on the float side). The toilet tank will take less water to fill.
• Buy a water saving flush button on the toilet.
• Please check whether your toilet continues to run after flushing. This can cost you about
25 liters per hour, or 219,000 liters of water per year!
Hygiene
- Use a shower timer. So that you are aware of the time it takes for you to shower.
- Turn off the tap while lathering your hands and brushing your teeth.
- Put an excess flow valve on your taps.
- Buy a water saving shower head.
Laundry and dishwashing
- Do not wash small loads, but instead wait for dirty clothing to collect. Wash with a well-filled (but not a fully packed) drum. For lightly soiled laundry use a shorter washing cycle.
- Are you washing the dishes by hand? Do not wash with running water. Do not pre-rinse and after-rinse too long.
- Are you using a dishwasher? Then you do not need to pre-rinse. The dishwasher has a pre-rinsing program. Run only full dishwashers.
Other tips
- Replace leaky faucets; they waste an average of 2000 liters of water per year.
- Regularly check your water meter. So you can detect in time if there is a leak somewhere in your water installation.
Tips around the house
- Save water when washing the car? Don’t use the garden hose and use a bucket instead. The garden hose easily uses 150 liters of water; with four 10 liter buckets this is also possible. Do you still really want to use a ‘spray’? Then use a pressure washer. A garden hose uses around 3,000 liters of water per hour, while the pressure washer uses 600 liters of water per hour. In addition, you’ll work faster with a pressure washer. You will save about 15 % of your time and therefore also water.
- Do not waste rainwater! You can collect rainwater in drums or in underground water tanks. Use it for the garden or for topping up your swimming pool.
- One liter of spilled oil can pollute one million liters of groundwater. So, be careful when working with motor oil.
- Mulch around plants with leaves, woodchips or gravel. So there will be less evaporation and the ground stays moister.
- Thinking about building a swimming pool? Think for a moment about the size. Especially in dry periods, the pool will need to be topped up regularly.
Saving electricity
By using your electrical appliances wisely, you can save significantly on energy bills. In this way a family with two children will save tens of dollars per year when using the washing machine, using a full load instead of a half full load. And ask yourself: a dryer is necessary at all in our sunny climate?
Switched off instead of stand-by
There are yet more ways to save! Switch off your electronic devices as far as possible instead of on standby. This can greatly reduce electricity consumption. Think about phone chargers, baby monitors and toothbrushes. And televisions, computers and audio systems.
Electricity guzzlers
Devices that need to warm up like microwaves, rice cookers, irons and hairdryers use lot of power. And did you know that the vacuum cleaner is one of the largest electricity guzzlers?
Energy efficient bulbs
Incandescent bulbs, where available, have a relatively high energy consumption. There are more and more types of energy efficient bulbs. LED lights are more energy efficient. Led lights consume up to 85% less energy than a comparable incandescent bulb. Moreover, the life span is 50 times longer.
We can now no longer do without many devices, but handling these wisely doesn’t take a lot of effort, and can easily save you tens of dollars.
Download our folder Saving (pdf). Or read the tips below.
Hidden
Hidden
Tips in the house
Refrigerator and freezer
- Make sure your refrigerator and freezer doors are closed. Always shut the doors as quickly as possible.
- Place your refrigerator and freezer in a coolest possible place.
- Maintain a constant temperature of 4 to 6 degrees Celsius in your refrigerator, in the freezer -18 degrees.
- Defrost your freezer regularly.
- A full refrigerator consumes less energy than an empty one.
Tip: fill the refrigerator with bottles of water. They retain the cold, as a result of which the refrigerator turns on less often. Also for the freezer applies: full is more energy efficient than empty.
Lightning
- Make maximum use of natural light.
- Use light bulbs that are energy efficient, such as LEDs or CFLs. Think about the Christmas lights, too!
- Turn the light off immediately when you leave a room.
Air conditioning and fan
- Combine the use of air conditioning and fan. The fan provides optimal spread of the cooled air.
- Choose an inverter air conditioner to save energy. An inverter air conditioning reaches the desired temperature four times faster than a conventional air conditioning.
Other devices
- Always iron several garments at once. An iron consumes the most power while heating up.
- Consider sweeping, instead of using the energy consuming vacuum cleaner.
- Cooking with gas stove is significantly more energy efficient than induction, ceramic or electric stoves.
Tips around the house
- Do you have outdoor lighting? Then use LED lights. When you place a photocell by your outdoor lights, they will turn on automatically at dusk and switch off at sunrise.
- Do you want to save more energy, use LEDs with motion detectors.
- Consider the energy consumption when buying your pool pump and drip system.
- Electric garden tools use a lot of energy. You could use a rake, instead of a leaf blower.
Insulation
In the case of insulation, we usually think of the cold. But good insulation is also very effective in keeping heat outside and coolness inside.
- When building or remodeling, install wall and roof insulation. This reduces the air conditioning and ventilation costs.
- Prevent the cool air from the air conditioning from escaping. Place rubber strips under doors. Check the seals of the window frames and, if required, apply a silicone sealant.
- Tinted glass delivers savings, especially with larger doors and windows.
- Double glazing keeps the heat outside.

